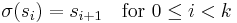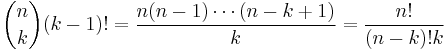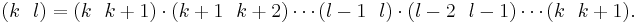Cycle (mathematics)
In mathematics, and in particular in group theory, a cycle is a permutation of the elements of some set X which maps the elements of some subset S to each other in a cyclic fashion, while fixing (i.e., mapping to themselves) all other elements. For example, the permutation of {1, 2, 3, 4} that sends 1 to 3, 2 to 4, 3 to 2 and 4 to 1 is a cycle, while the permutation that sends 1 to 3, 2 to 4, 3 to 1 and 4 to 2 is not (it separately permutes the pairs {1, 3} and {2, 4}). The set S is called the orbit of the cycle.
Contents |
Definition
A permutation of a set X, which is a bijective function 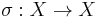 , is called a cycle if the action on X of the subgroup generated by
, is called a cycle if the action on X of the subgroup generated by 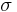 has exactly one orbit with more than a single element. This notion is most commonly used when X is a finite set; then of course the orbit S in question is also finite. Let
has exactly one orbit with more than a single element. This notion is most commonly used when X is a finite set; then of course the orbit S in question is also finite. Let 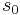 be any element of S, and put
be any element of S, and put 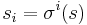 for any
for any 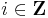 . Since by assumption S has more than one element,
. Since by assumption S has more than one element, 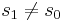 ; if S is finite, there is a minimal number
; if S is finite, there is a minimal number 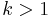 for which
for which 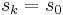 . Then
. Then 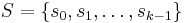 , and
, and 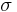 is the permutation defined by
is the permutation defined by
and 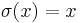 for any element of
for any element of 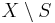 . The elements not fixed by
. The elements not fixed by 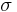 can be pictured as
can be pictured as
 .
.
A cycle can be written using the compact cycle notation 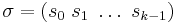 (there are no commas between elements in this notation, to avoid confusion with a k-tuple). The length of a cycle, is the number of elements of its orbit of non-fixed elements. A cycle of length k is also called a k-cycle.
(there are no commas between elements in this notation, to avoid confusion with a k-tuple). The length of a cycle, is the number of elements of its orbit of non-fixed elements. A cycle of length k is also called a k-cycle.
Basic properties
One of the basic results on symmetric groups says that any permutation can be expressed as the product of disjoint cycles (more precisely: cycles with disjoint orbits); such cycles commute with each other, and the expression of the permutation is unique up to the order of the cycles (but note that the cycle notation is not unique: each k-cycle can itself be written in k different ways, depending on the choice of 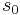 in its orbit). The multiset of lengths of the cycles in this expression is therefore uniquely determined by the permutation, and both the signature and the conjugacy class of the permutation in the symmetric group are determined by it.
in its orbit). The multiset of lengths of the cycles in this expression is therefore uniquely determined by the permutation, and both the signature and the conjugacy class of the permutation in the symmetric group are determined by it.
The number of k-cycles in the symmetric group Sn is given, for 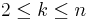 , by the following equivalent formulas
, by the following equivalent formulas
A k-cycle has signature (−1)k − 1.
Transpositions
A cycle with only two elements is called a transposition. For example, the permutation of {1, 2, 3, 4} that sends 1 to 1, 2 to 4, 3 to 3 and 4 to 2 is a transposition (specifically, the transposition that swaps 2 and 4).
Properties
Any permutation can be expressed as the composition (product) of transpositions—formally, they are generators for the group. In fact, if one takes 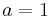 ,
, 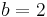 , ...,
, ..., 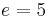 , then any permutation can be expressed as a product of adjacent transpositions, meaning the transpositions
, then any permutation can be expressed as a product of adjacent transpositions, meaning the transpositions 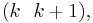 in this case
in this case 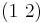 ,
, 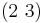 ,
, 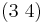 , and
, and 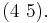 This follows because an arbitrary transposition can be expressed as the product of adjacent transpositions. Concretely, one can express the transposition
This follows because an arbitrary transposition can be expressed as the product of adjacent transpositions. Concretely, one can express the transposition 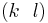 where
where 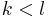 by moving k to l one step at a time, then moving l back to where k was, which interchanges these two and makes no other changes:
by moving k to l one step at a time, then moving l back to where k was, which interchanges these two and makes no other changes:
In fact, the symmetric group is a Coxeter group, meaning that it is generated by elements of order 2 (the adjacent transpositions), and all relations are of a certain form.
One of the main results on symmetric groups states that either all of the decompositions of a given permutation into transpositions have an even number of transpositions, or they all have an odd number of transpositions, that allows to define the parity of a permutation.
See also
- Cycles and fixed points
- fifteen puzzle
- symmetric group
- transposition
- group
- subgroup
- dihedral group
- cycle detection
External links
References
- Anderson, Marlow and Feil, Todd (2005), A First Course in Abstract Algebra, Chapman & Hall/CRC; 2nd edition. ISBN 1584885157.
- Fraleigh, John (2002), A first course in abstract algebra (7th ed.), Addison Wesley, ISBN 978-0201763904
This article incorporates material from cycle on PlanetMath, which is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License.
This article incorporates material from transposition on PlanetMath, which is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License.